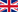
Aubergines - history, production, trade
The aubergine, whose scientific name is Solanum Melongena, is a fleshy berry with a whitish and spongy flesh, often with a spicy and bitterish taste; inside the flesh of this fresh vegetable there are more or less numerous flat white, amber or yellow seeds.
The plant of aubergine belongs to the family of Solanaceae, to which belong also other fruit and vegetable products such as potatoes, peppers and tomatoes: to this family of plants, in fact, belong at least 85 genus and 2,200 species of different plants.
The aubergine is a typical Mediterranean vegetable, because it is a fruit and vegetable product that needs a mild clime to grow and develop completely. The most worthwhile season as to production of aubergines is summer: more precisely, this fresh fruit and vegetable product can be found between June and September; August is instead the perfect month for the harvest and the consumption of fresh aubergines.
When buying aubergines , you have to pay attention that the petiole (or peduncle) is still attached to the vegetable (in some varieties of aubergines, the petiole is bright green, while in other varieties it is bronze-black) and that it does not have withered parts.
The skin of aubergines is smooth and tense: the lack of bruises, black parts or rotten parts usually means that the vegetable is fresh.
The flesh of aubergines must be firm at touch, not hard (because it would not be ripe), but also not too much soft (because it would mean that the aubergine is overripe, and it would be stringy and too bitter).
The presence of a small protuberance at the base of the aubergine usually means that the flesh of this fresh vegetable is compact and with few seeds.
Aubergines can be stored in the refrigerator for 4-5 days: for the storage in the refrigerator, it is better if the aubergine is whole and has still the petiole; furthermore, aubergines can be frozen in slices, after being boiled in water for some minutes.
The aubergine is a fruit and vegetable product that is consumed only after being cooked: raw, in fact, the aubergine contains solanine, a poison present also in potatoes and in green tomatoes; if eaten it can cause headache, nausea and vomit; furthermore, the aubergine is bitter and unpleasant if consumed raw.
After being cooked the aubergine is a very versatile vegetable: it can be used in many ways in cuisine, as an appetizer, a first course, a second course and as a side dish (such as for example the very popular “parmigiana" of aubergines, the stuffed aubergines or the aubergines in oil and in vinegar).
The aubergine is a fruit and vegetable product that can be consumed both with and without the skin, according to the preparations chosen and to the composition of the dish.
It is better, before cooking aubergines, to discharge their water, so that they will lose their typical bitter taste: it is enough to salt aubergines (better with coarse salt) for some hours; when they will have lost the water, aubergines must be rinsed and dried, to be ready for fresh consumption after cooking or to any other cuisine processing.
The aubergine, as it is a fruit and vegetable product with low nutritional values, is low also in calories and fats, proteins, carbohydrate and sugars; for this reason, the aubergine is largely recommended in slimming diets, as it enhances the decrease of cholesterol levels in blood.
However, as mentioned before, it is necessary to pay attention while preparing aubergines; in fact, as their flesh is quite spongy, these fresh vegetables perfectly absorb any dressing (and food fats such as oil), that can be, unlike the aubergine, very rich in calories. The aubergine is therefore suitable to low-calorie diets if, for example it is grilled or boiled; at the same time it is an ideal vegetable as an ingredient for very tasty and rich in calories dishes.
With its few calories (only 18 Kcal per 100 gr. of product), the aubergine is also very rich in water (which enhances the activity of kidneys), in potassium (which provides mineral salts, above all in Summer), in vitamin C and A, in phosphorus, calcium and tannins.
Among the typical characteristics of aubergines there are their purifying and diuretic properties that are among the first advantages for the body brought by aubergines; furthermore, aubergines are considered mild laxatives.
The skin of aubergines contains beneficial substances for the liver, the pancreas and the intestine, as they stimulate the production and the elimination of bile; furthermore, as this fruit and vegetable product does not contain gluten, aubergines are perfect also for people suffering from celiac disease.
The flesh of aubergines is used in cosmetics, in the preparation of face creams and masks.
The beneficial properties of this fresh vegetable are countless: aubergines , apart from the characteristics mentioned above, are also used as a traditional domestic remedy because they have a nutritional effect on the skin: it is enough to mash the flesh of aubergines and to put it on the face, alone or preferably mixed with yoghurt, to enhance its beneficial effect.
Aubergines become increasingly important: nowadays, there are many companies that produce aubergines, certified companies for the production of aubergines, producers of aubergines, companies that produce organic aubergines, companies that deal with the trade of aubergines (packaging of aubergines), retailers of aubergines, importers of aubergines, exporters of aubergines and wholesalers of aubergines.