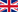
The plant and the production of Melons
The melon is an annual herbaceous, climbing plant: its roots are sinewy and can extend in the soil for more than 150 cm.
The stem of the plant of melon is branched and haired.
Leaves of the plant of melon are alternate, long more than 10 cm; the petiole is 10 cm long.
The flowers of the plant of melon are yellow and five-lobed, usually monoecious, where sexes are separate on two different flowers; in general firstly appear male flowers, grouped in inflorescences, and later feminine flowers.
The crossed fecundation of the plant of melon takes place through insects in the cultivations of melons in open fields; instead, it is better to use artificial fecundation for those plants of melons that are cultivated in greenhouses.
The plant of this fresh fruit has a large flowering that lasts throughout all the Summer, from May to September: however, only the 10% of these flowers become fruits.
The fruit of melon is an epigynous berry, usually large, that can be ovoid or roundish and usually has a skin on which there are several lines that are similar to slices. In general the skin of melons is smooth or slightly wrinkled, and its colour can vary from a light yellow to different tones of green.
The colour of the flesh of melons, instead, can vary from white to orange; the flesh is very juicy and flavoured when it has just ripened. Inside the fruit there is a central hole, which is stringy and contains many seeds.
The plant of melons is sown in April-May in one-meter distant rows, as this is a plant as this is a plant with fibrous root that can become quite long. In general seeds should be kept at a distance of about 40 cm.
As to the early cultivations of melons, the seeding is done in March in the seedbed, on a hot bed, transplanting seedlings later in open fields, when the temperature is adequate.
The melon can also be cultivated in heated greenhouses, sowing in December and transplanting the plants, in the greenhouses in January.
The world production of melons is quite large and it is about 27 million tons each year (data 2010).
The major world producers of this fruit are: China, that alone produces about the 52% of the entire world production of melons, Turkey, the United Stated, Morocco, Israel, Iran, Egypt and India.
In Europe the major producers of melons are instead Spain (with about one million tons of this fresh fruit produced), Italy (with almost 600,000 tons of melons produced), France (with an average production of 300,00 tons of melons) and Romania.
Since 2000, in Italy have begun many imports of Yellow melon, produced in some Brazilian companies: this product is imported from October to April, guaranteeing the coverage of the winter months when this fruit and vegetable product does not develop in Italy
The exports of melons from Brazil for such a long period is guaranteed by some companies present in the Salvador region.