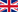
The production process of Fourth Range Products
The preservation of organoleptic qualities of products depends on the processing procedures, on the preservation techniques used and on the time necessary in order to make the product reach the dealer, passing from the processing plant.
Fresh vegetables, before being traded and consumed, can be subject to a number of technological treatments, all strictly thought not to compromise the natural characteristics of freshness and naturalness of these vegetable products.
The preservation of fourth range fruit and vegetable products must be based on a combined action of different treatments, with the common aim to prevent bacteria to attack and to delay the appearance of alterations.
The steps of the fourth range fruit and vegetable products production are:
- Selection: the vegetables assigned to be sliced or peeled and stored for different time must necessarily be of excellent quality; major requirements concern the variety choice (only vegetable with specific structural, metabolic and composition characteristics) and a careful choice of suppliers (list of requisites concerning cultivation operations, harvesting and post-harvesting in order to avoid microbial contaminations).
- Cleaning and washing: products must be washed in specific tanks, built with waterfall, perfusion, and bubbling (with the water moving through mechanical or air agitators) washers, with or without descaling brushes (according to the more or less hardness of the vegetable).
During this phase, the factors that have an important role in reducing levels of contaminations of fruit and vegetable products, concern the water quality (must be drinkable), water temperature (<5°C), water turbulence (it helps the detachment of bacteria and solid particles), and the water quantity (5-10 l/kg of product before cutting and 3-5 l/kg after cutting). - Cutting: phase of processing of the product when the edible part is cut in slices or cubes. This step makes the vegetable product more subject to alterations as a consequence of the increase of the cellular metabolism (breathing) and of the exposition of non-protected area to microbial enzymes.
- Washing and drying: another washing of the product to ascertain the absence of bacteria, which could easily develop on the product, thanks to the availability of cellular juices freed with the cutting.
- Packaging: it is a fundamental phase of the preservation process of fourth range products, essential to keep the characteristics of freshness for all the shelf life of the product. Its aim is to protect vegetables from mechanical actions, to value the quality and to encourage the purchase by the final consumer. The modalities of packaging have a fundamental role in lengthening the preservation capacity of vegetables.
The packaging in a modified atmosphere offers all the possibilities to reach an important increase of the shelf life of the fourth range product without losing the characteristics of the fresh product: the preservation capacity of the fresh product is in fact lengthened with an atmosphere that slows the degrading processes, as the increasing of microbial organisms, and increasing at the same time the developing of some positive effects.
Basically temperatures between 5 and 10 °C are used, because some fresh vegetable varieties can be damaged by cold.
- Labelling: processing phase of the fourth range product in which the information regarding the cultivation and production of the vegetable are put on the label. In fact, reading the labels of fourth range products makes the consumer aware of the history of that specific product. Regulations governing labelling of the 4th range products are a form of guarantee and protection of the consumer: for this reason, consumers should be able to properly read information on labels of every fourth range fruit and vegetable product, in this way they would be able to take conscious decisions when purchasing these products.
In fact, the key objective of the regulation is to provide, through a punctual and rigorous labeling, an accurate description of the product, of its components, ingredients, nutritional values and of the functions that they can play.
- Retailing and transport: in order to maintain the final quality of fourth range fruit and vegetables, organic products or even integrated products, it is crucial to minimize the elapsing time between harvesting and processing: seeding is, therefore, programmed to get stocks to the establishments, in a continuous but staggered way, being particularly careful to the modality of preservation during transport of fourth range products: it is fundamental to control the balance between carbon dioxide and oxygen and to keep the right moisture level inside the package.
- Sale;
- Storage;
Companies can assure that all the processing of fourth range products, from selection of the product to the transport and the sale, is done within 24 hours: usually from the camp of the producer of the fruit and vegetable product to the completion of the processing phase pass 6-7 hours and other 17-18 hours in order to make the product reach the retailers.